Optical tweezer
Optical tweezers can be used to capture and move the smallest objects in a targeted manner. This manipulation is possible by moving microscopic particles through the electromagnetic field of a laser in the direction of the location with maximum light intensity. In biophotonics, this technique is particularly applied to cells, which can also be sorted with it.
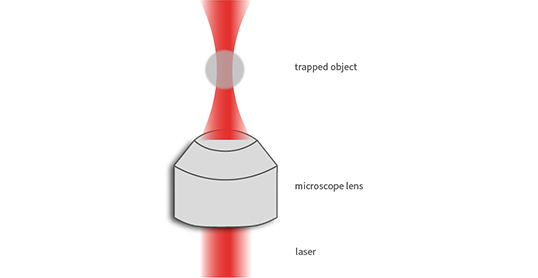 For a simple and widely used implementation of optical tweezers, a laser beam is coupled into an optical microscope, which is thereby focused in the object plane. When selecting the laser, care must be taken to ensure that the particles to be manipulated are transparent to the selected wavelength and that the laser has a Gaussian profile. Once the particle to be gripped is introduced into the focal point, any deviation will result in a restoring force into the focal point and the particle will be in an optical trap.
For a simple and widely used implementation of optical tweezers, a laser beam is coupled into an optical microscope, which is thereby focused in the object plane. When selecting the laser, care must be taken to ensure that the particles to be manipulated are transparent to the selected wavelength and that the laser has a Gaussian profile. Once the particle to be gripped is introduced into the focal point, any deviation will result in a restoring force into the focal point and the particle will be in an optical trap.
Often, such a setup is supplemented with a second laser of a different wavelength, which serves as a laser scalpel for processing the particles. More complex, holographic optical tweezers use multiple controllable focal points that can be created and also moved via a spatial light modulator (SLM). This makes it possible not only to capture a particle, but also to move or align it.
Back to the Application Biophotonics